
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss on the
scalp and other parts of the body.
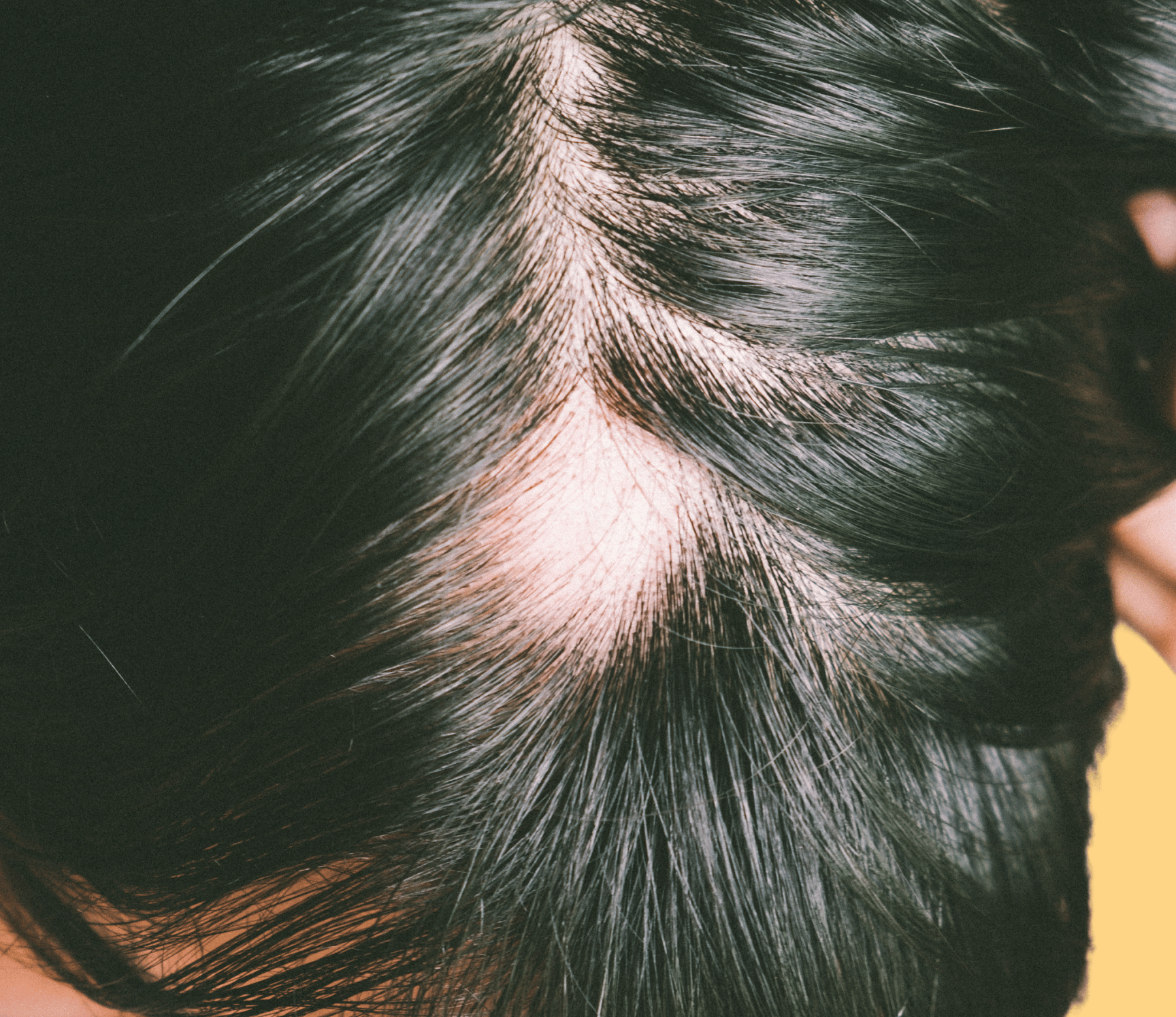
Alopecia areata is a common condition that affects people of all ages and can occur at any time. It is characterized by sudden, patchy hair loss and can range from mild to severe. In some cases, alopecia areata can progress to complete hair loss, known as alopecia totalis.
The exact cause of alopecia areata is not fully understood, but it is
believed to be related to an autoimmune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the hair
follicles. Other factors that may contribute to the development of alopecia areata include genetics, stress, and
hormonal imbalances.
The main symptom of alopecia areata is patchy hair loss on the scalp, but it
can also affect other parts of the body. The hair may fall out suddenly, leaving smooth, round patches on the
scalp. In some cases, the hair may regrow on its own, while in others it may remain permanently missing.
There is no cure for alopecia areata, but there are several treatments that
can help manage the symptoms and promote hair regrowth. These include topical corticosteroids, minoxidil,
anthralin, and immunotherapy. In some cases, hair transplantation may also be an option. Additionally, managing
stress and maintaining a healthy diet can also help improve overall hair health.
It is important to consult a dermatologist if you experience sudden hair
loss or patches of baldness, as they can diagnose the condition and provide an appropriate care plan. Early
diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of hair regrowth and prevent further hair loss.